Mar 28 2023

Exploring NFT Marketplace Business Models - Choose the right one
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are unique digital assets that have taken the world by storm, with the market growing rapidly as more people understand their value. NFT marketplaces, in turn, have become a hub for buying and selling these digital assets. As a result, numerous NFT marketplaces have emerged to meet the demand for buying and selling these tokens.
Simply put, an NFT marketplace is a platform that allows users to buy, sell, and trade NFTs. These marketplaces provide a secure and efficient way for creators to monetize their digital assets and for collectors to acquire unique and valuable pieces.
As the NFT market continues to grow, investors need to understand the different business models NFT marketplaces can employ and how they differ in revenue generation, user experience, and value proposition. Choosing the right business model is crucial for the success of an NFT marketplace. Each model has unique benefits and drawbacks, and choosing the one that aligns with your goals and objectives is important.
NFT businesses and Marketplaces the numbers game
According to research by global research firm VMR (Verified Market Research), the overall value of the NFT market is expected to rise to $231 billion by 2030. There are more than 20 NFT marketplaces worldwide, and thousands of NFT transactions occur daily, with weekly sales ranging from $15,000 to $50,000. OpenSea and CryptoPunks are the two most prominent NFT marketplaces, representing 35.32% and 26.84% of the trading volume, respectively.
Business Models of NFT Marketplaces
The NFT marketplace business model revolves around creating a platform for buying and selling NFTs representing digital assets such as artwork, music, videos, virtual real estate, and other forms of digital content.
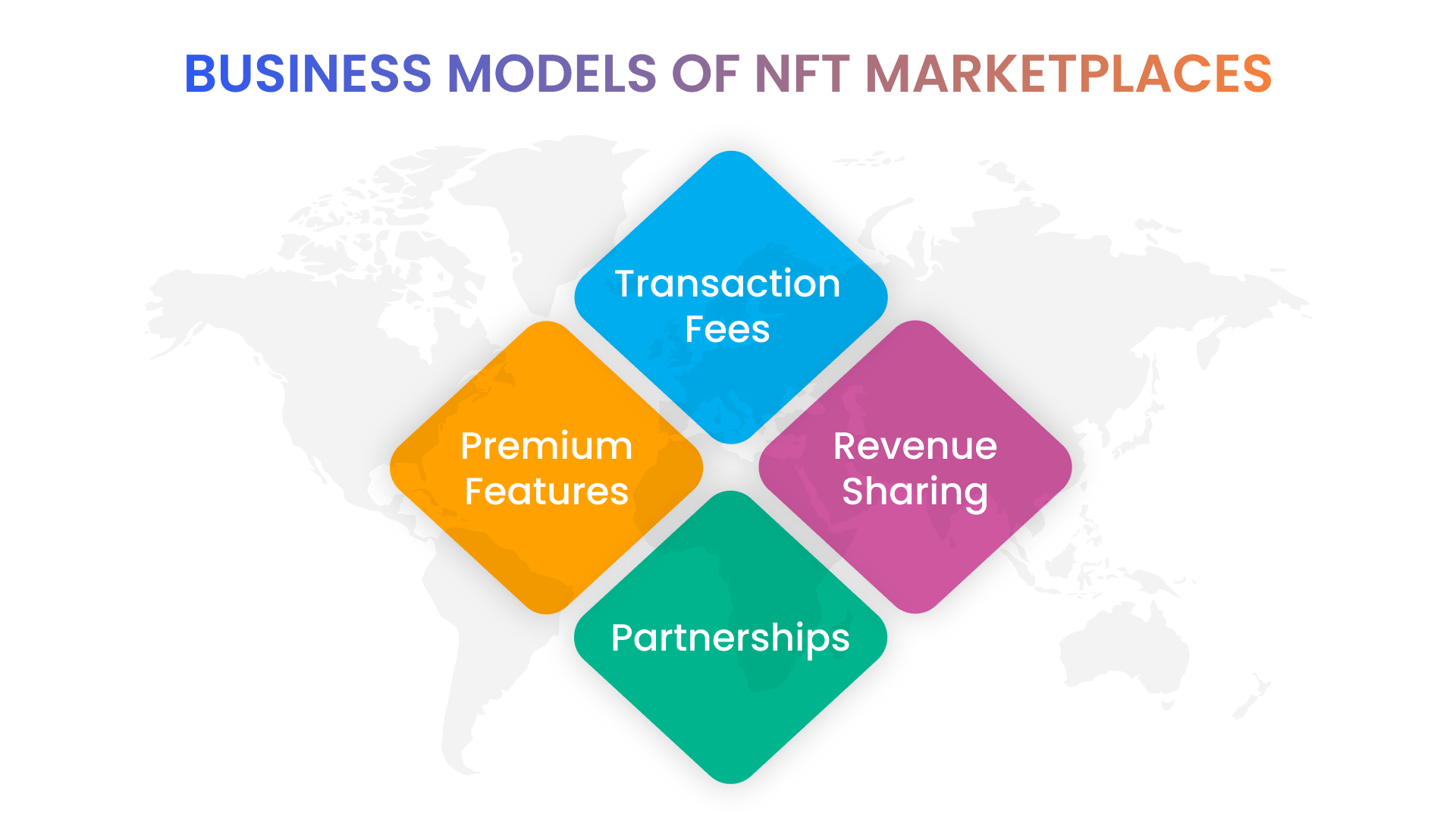
The NFT business model is primarily based on transaction fees, premium features, partnerships, and the ability to offer artists a new revenue stream for their digital works. Here's a more detailed breakdown of these revenue streams:
Transaction Fees: NFT marketplaces generate revenue by charging a fee for each transaction made on their platform. These fees are typically a percentage of the sale price, ranging from 2.5% to 10%.
Premium Features: Some marketplaces offer premium features or services for a fee. For instance, a marketplace might charge a fee to feature an NFT more prominently or provide additional tools for managing NFT collections.
Partnerships: NFT marketplaces can generate revenue through partnerships with artists or brands. The marketplace could receive a percentage of the sale price for each NFT sold or charge a licensing fee for using the artwork or intellectual property.
Revenue Sharing: Some NFT marketplaces offer revenue-sharing arrangements with artists or creators. In these cases, the marketplace receives a percentage of the revenue generated by the NFT sales, while the artist receives the majority of the revenue.
The architecture of an NFT marketplace typically involves a blockchain-based platform that leverages smart contracts to manage the buying and selling of NFTs. The blockchain provides a decentralized ledger that ensures transparency, immutability, and security in the transactions made on the platform. They eliminate the need for intermediaries like banks or lawyers, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. NFT marketplaces can be built on various blockchain platforms, including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, or Flow.
Discover more about blockchain app development here!
Different Types of NFT Marketplace Models
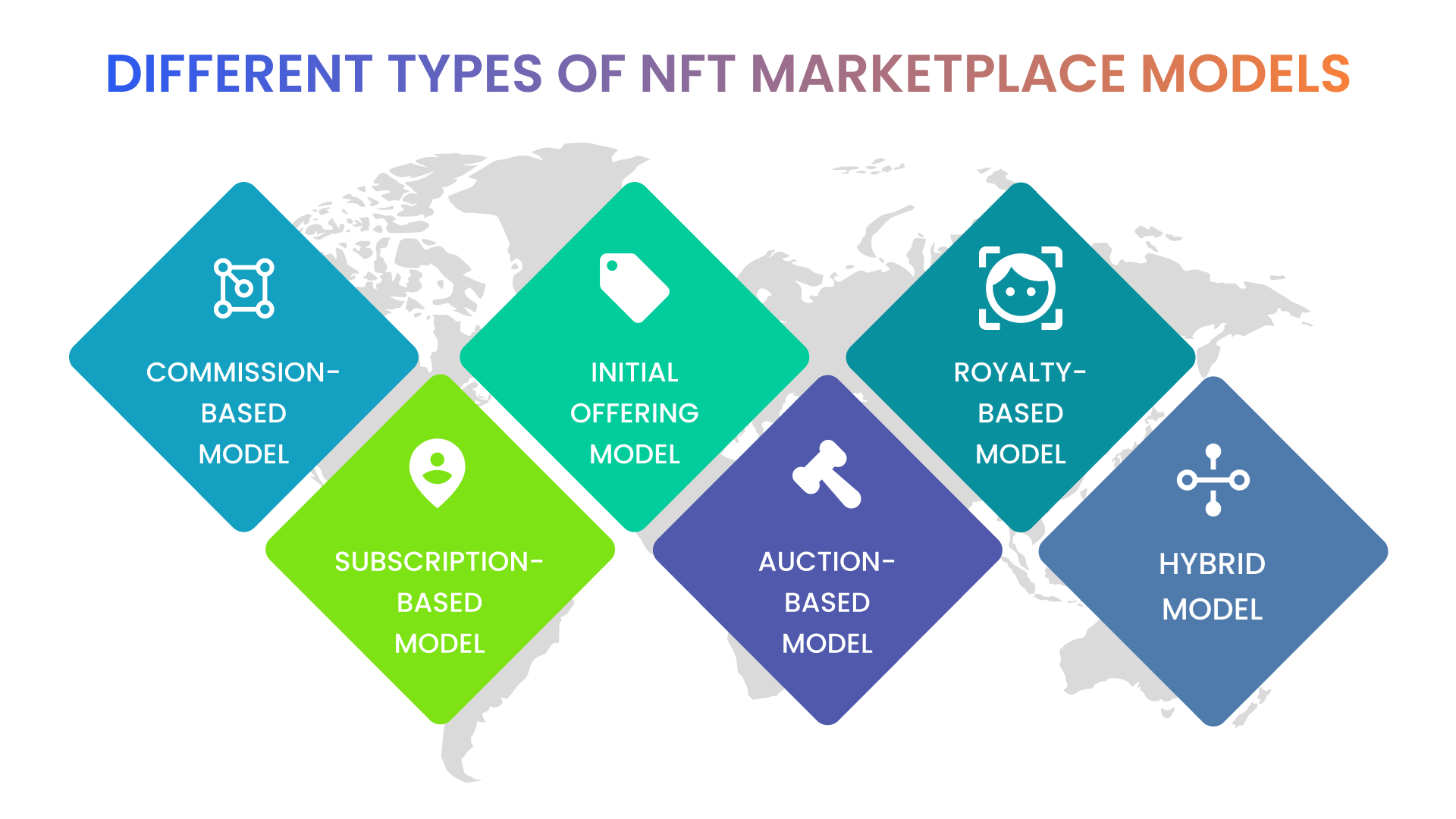
Commission-based Model:
The commission-based model is one of the most common business models for NFT marketplaces. In this model, the marketplace charges a fee or percentage of the transaction amount for each sale on the platform.
How the commission-based model Works
The NFT marketplace takes a percentage of each sale made on the platform.
This model incentivizes the marketplace to promote high-quality assets and ensure fair transactions.
The percentage commission charged by the marketplace can vary, ranging from as low as 2.5% to as high as 20%.
Examples of Marketplaces:
OpenSea: OpenSea is one of the largest NFT marketplaces and employs a commission-based model, charging a 2.5% commission on all sales made on the platform.
Rarible: Rarible is another popular NFT marketplace that uses a commission-based model, charging a 2.5% commission on sales.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: This model provides a straightforward revenue stream for the marketplace without taking on the risks associated with owning the assets. The model also incentivizes the marketplace to promote high-quality assets and ensure a fair transaction.
Cons: The marketplace may be seen as an intermediary between the buyer and seller, which could lead to distrust. The commission-based model could also lead to higher prices for buyers, as sellers may increase their prices to offset the commission.
How Oaktree Solutions Can Help:
Oaktree solutions can help NFT marketplaces implement this business model by providing a reliable, secure, and scalable platform for users to buy and sell NFTs. We also offer customized solutions for handling payments, tracking sales, and managing commissions, ensuring a seamless and hassle-free user experience.
Subscription-based Model:
In the subscription-based model, the marketplace charges a monthly or annual fee for users to access certain features or services on the platform. For example, a premium subscription may provide the following:
Exclusive NFT drops.
Early access to new releases.
Special discounts on transaction fees.
How it Works:
In the Subscription-Based Model, users pay a recurring fee to access the NFT marketplace.
The marketplace may offer different tiers of subscriptions, each with different features and benefits.
This model provides a predictable revenue stream for the marketplace and encourages user loyalty.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: The Subscription-Based Model provides a predictable revenue stream for the marketplace and encourages user loyalty. It also allows the marketplace to offer additional features and benefits to subscribers.
Cons: The subscription fees may deter some users from using the marketplace, and the marketplace must continue to provide value to justify the subscription fee.
Explore The Diverse NFT Marketplace Models
Connect with our experts today to discover the various types of models and find the perfect fit for your NFT venture
Talk To Our ExpertsExamples of Marketplaces:
Nifty Gateway: Nifty Gateway is an NFT marketplace that offers a subscription-based model, with different tiers of subscriptions offering different features and benefits.
KnownOrigin: KnownOrigin is another NFT marketplace that offers a subscription-based model with additional benefits for subscribers.
Initial Offering Model:
The initial offering model is a unique approach to NFT marketplaces. In this model, the marketplace partners with an artist or creator to launch an exclusive NFT drop on the platform. The NFTs are sold for a limited time or until a specific number of tokens are sold.
How it Works
In the Initial Offering Model, the NFT marketplace creates and sells its own NFTs through a public sale or an auction.
The initial offering model allows the marketplace to generate buzz and excitement around a particular NFT release while creating a sense of exclusivity for buyers.
The marketplace retains ownership of the NFTs and can set the initial price and terms of the sale.
It provides a unique revenue stream for the marketplace, as they can profit from selling their assets.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: The Initial Offering Model allows the marketplace to generate revenue from the sale of its own assets without relying solely on commissions. It also provides a unique value proposition for the marketplace and can help differentiate it from competitors.
Cons: The marketplace is taking on the risk of creating and selling its own NFTs and may be unable to sell all the assets. This model also requires a significant investment in creating and promoting the assets.
Examples of Marketplaces:
NBA Top Shot: NBA Top Shot is a popular NFT marketplace that employs the Initial Offering Model. They create and sell their own unique NFTs, such as digital collectibles of iconic basketball moments.
SuperRare: SuperRare is another NFT marketplace that uses the Initial Offering Model to create and sell unique NFTs.
Auction-based Model:
The auction-based model is another popular business model for NFT marketplaces. In this model, NFTs are sold through an auction system, with users placing bids on the NFTs they are interested in. The auction can last for a set amount of time, with the highest bidder at the end of the auction winning the NFT.
The auction-based model can help to drive up the value of NFTs by creating competition among buyers. However, this model can also be challenging for buyers who may be outbid at the last minute or for sellers who may not receive the price they were hoping for.
Examples of auction-based NFT marketplaces include Nifty Gateway and Foundation.
Royalty-based Model:
A royalty-based model is a unique approach to NFT marketplaces that focuses on long-term revenue generation for creators. In this model, the artist or creator of an NFT receives a percentage of the transaction amount generated from each subsequent sale of their NFT. Each time the NFT is sold or resold on the platform. This model aims to provide ongoing revenue for artists and creators, even after the initial sale of the NFT.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: The Royalty-Based Model provides an additional revenue stream for NFT creators and incentivizes them to create high-quality assets that retain value over time. It also promotes a more fair and equitable system for creators, who can continue to benefit from their work even after the initial sale.
Cons: This model may require additional technical infrastructure to track resales and ensure royalty fees are paid to the NFT creators. It may also lead to higher prices for buyers, as sellers may increase their prices to offset the commission and royalty fees.
Hybrid Model:
Finally, some NFT marketplaces are adopting a hybrid approach that combines elements of multiple business models. For example, a marketplace may offer both commission-based sales and initial offering sales, or a marketplace may offer both subscription-based access to premium features and royalty-based revenue for creators.
The hybrid model can allow NFT marketplaces to diversify their revenue streams and appeal to a broader range of users and creators. However, managing the different business models effectively may also require more complex systems and operations.
Checklist for NFT Marketplace Business Model
Starting an NFT marketplace requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some key elements to include in your NFT marketplace business model:
User-friendly platform: Your NFT marketplace should be easy to navigate, with clear instructions for buying and selling NFTs.
Smart contract integration: Smart contracts ensure secure and transparent transactions. Make sure your platform integrates with a reliable smart contract platform.
Robust search and filtering: Users should be able to easily find the NFTs they are looking for through search or advanced filtering options.
Strong community support: Building a strong community around your NFT marketplace is essential for long-term success. Encourage user engagement and provide excellent customer support.
As the NFT market continues to grow and evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative business models that reflect the unique features and benefits of NFTs. As a dedicated software solution provider, we can help potential investors develop and implement NFT marketplace solutions that align with their specific goals and objectives. Our software solutions can help potential investors in NFT marketplaces succeed by providing reliable, secure, and scalable platforms tailored to their specific business models and goals.

